There are various methods for measuring temperature, but what exactly is a "temperature sensor," a contact thermometer that uses heat conduction from the object being measured?
Temperature sensors that are widely used to measure temperature in testing and research sites, as well as production sites such as factories, are generally called thermocouples or resistance thermometer thermometers.
What is a thermocouple?
When a closed circuit is made with two different metal wires and the two contact at both ends are kept at different temperatures, current flows that corresponds to the temperature difference (Seebeck effect).
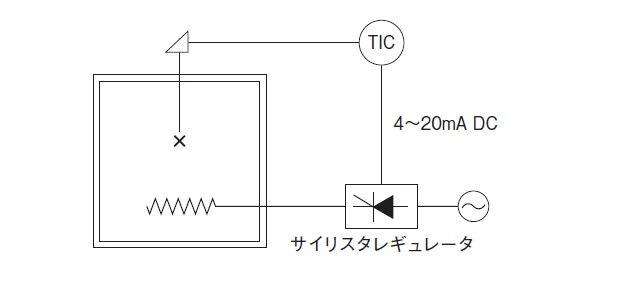
One end of this wire is cut open to create two terminal, which are then connected to a DC voltage to measure the thermoelectromotive force, allowing the temperature to be measured. A thermocouple (wire) is a combination of two types of metal that uses this principle to measure temperature. The JIS standard specifies K, R, B, S, T, E, J, and N.
For example, in the case of a K thermocouple, when the measurement contact 200°C and the reference contact is 0°C, a voltage of 8.138 mV is generated.
- structure
A thermocouple configuration of a thermocouple wire, an insulation tube, a protective tube, a terminal box, etc.
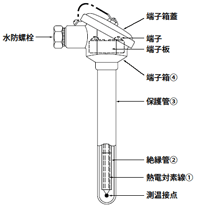
- Thermocouple wire: Two types of metal wire that make up both legs of a thermocouple, with the ends welded together. For example, a K thermocouple has a (+) leg made of an alloy mainly made of nickel and chromium, and a (-) leg made of an alloy mainly made of nickel.
- insulation tube: Used to prevent short circuits between thermocouple wires. Usually, a heat-resistant porcelain tube is used.
- Protective tubes are used to protect temperature measuring contact and thermocouple wires from the object being measured and surrounding gases, and are available in a variety of materials and shapes depending on the usage atmosphere and purpose.
- terminal box: Contains terminal that connect the compensating wires from instrument and the thermocouple. They are available in aluminum die-cast and phenolic resin.
- Thermoelectric Power Table
- Solid Pack Thermocouples
This thermocouple has an insulation material filled in the gap between the protective tube and the thermocouple wire. In addition to the insulation material, the use of a thick protective tube makes features to withstand long periods of continuous use in high temperatures and hostile environments. There are three types of standard protective tube diameters: Φ10, Φ15, and Φ22 mm.
- Sheathed Thermocouple
Like solid pack thermocouples, the gap between the protective tube and the thermocouple wire is filled with insulation material. The manufacturing method differs from that of solid pack thermocouples, and mainly because it is easy to make a thin protective tube, it has a fast response and is suitable for measuring the temperature of small objects in narrow spaces. There are nine types of protective tube diameters: Φ0.15, Φ0.3, Φ0.5, Φ1.0, Φ1.6, Φ3.2, Φ4.8, Φ6.4, and Φ8.0 mm.
- Compensating Wire
When the thermocouple terminal and the reference contact are separated, a temperature sensor is connected between them in place of the thermocouple to compensate for errors caused by temperature changes at the thermocouple terminal.
- Tolerance
The measurement temperature is classified according to the error range according to the JIS standard.
Example: K thermocouple
| class | Measurement temperature | Tolerance (℃) |
|---|
| 1 | -40℃ or higher and lower than 375℃
375℃ or higher but less than 1000℃ | ±1.5
±0.004×|t| |
| 2 | -40℃ or higher and lower than 333℃
333℃ or higher but less than 1200℃ | ±2.5
±0.0075×|t| |
| 3 | -167℃ or higher, less than 40℃
-200℃ or higher but lower than -167℃ | ±2.5
±0.015×|t| |
What is resistance thermometer?
The electrical resistance of metals increases or decreases with changes in temperature, and since there is a fixed relationship between temperature and electrical resistance, it is possible to know the temperature by measuring resistance. Temperature measuring elements that utilize this principle are called resistance thermometer, and generally use platinum as the wire material.
The JIS standard specifies Pt100, Pt500, and Pt1000, but Pt100 is generally used more frequently. Note that the old JIS standard JPt100 is still used in some places.
- Structure
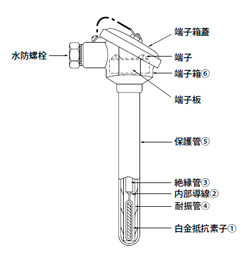
A platinum resistance thermometer configuration of a resistance element, an internal conductor, an insulation tube, a vibration-resistant tube, and a protective tube.
- Platinum resistance element: A thin platinum wire enclosed in a ceramic spool. The platinum wire is designed to be protected from distortion due to heat, and is small, has a fast response, and has good insulation.
- Internal conductor: A conductor that connects the resistance element and terminal. Normally, three nickel wires are used, which can eliminate the effects of conductor resistance.
- insulation tube: Used to prevent short circuits between internal conductors.
- Vibration-resistant tube: Made of brass, this is used to prevent damage to the resistance element due to vibration.
- Protective tube: Used to protect resistance element and internal conductors from the object being measured.
- terminal box: Contains the connection terminal that connect the wires from instrument to the internal wires.
- Sheathed resistance thermometer
The gap between the protective tube and the platinum resistance element is filled with insulation material. It is easy to make a thin protective tube, so it has a fast response and is suitable for measuring the temperature of small objects in narrow spaces. There are four types of protective tube diameters: Φ3.2, Φ4.8, Φ6.4, and Φ8.0 mm.
- Connecting wire
Conductor for connecting resistance thermometer to recorders, regulators, etc.
- Tolerance
The JIS standard classifies temperatures according to the error range of the measured temperature.
| class | Tolerance |
|---|
| AA | ±(0.1 + 0.0017 × |t|) °C |
| A | ±(0.15+0.002×|t|)℃ |
| B | ±(0.3+0.005×|t|)℃ |
| C | ±(0.6+0.01×|t|)℃ |
*For further details, please refer to the temperature sensor catalog.