| Sampling Period | Input signal capture interval |
| shunt resistor |
resistance that is connected between the (+) and (-) input terminal when using a 4 to 20 mA DC current input signal. Some models have a built-in shunt resistor. |
| output limiter |
A function to set the upper or lower limit higher limit value that can be output at control output (MV). |
| Output change limiter |
A function that limits the amount of change in the control output (MV). |
| Manual output operation |
A function to manually set the magnitude of the control output (MV). |
| scaling Function |
A function that converts the transmission signal (4 to 20 mA, 1 to 5 V) input from a sensor or device into an actual quantity (pressure, flow rate, humidity, etc.) and display instead of display it as a raw value. |
| step |
Used for control in which the set value (SV) is changed over time in a program controller. The required time and the set value (SV) after the time has elapsed are set in step, and a control pattern is configuration by combining multiple step. |
| Control Period |
The time required to change the output value of control output (MV). |
| direct operation |
As the measured value (PV) increases and approaches the set value (SV), control output ratio also increases. Used to control refrigerators, etc. |
| Accuracy ratings |
The precision with which the input signal is taken in and converted into a numerical value. |
Setting Value
(Setting Value) |
control target value |
| contact |
current The function of the device is to conduct or interrupt the relays and switches. contact The different operations that a contact, b contact, and c contact have are divided into a , b , and c , respectively.
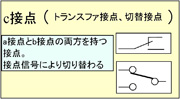 From JIS C0617-7 "Electrical Graphic Symbols" |
| sensor compensation |
A function that adds a correction value to the measured value (PV) obtained from the input signal and display it. |
| operation terminal |
A device that operates by receiving the control output from a controller. It refers to thyristor regulators, control valves, etc. |
Measurements
(Process Variable) |
The value read from the input signal |
| Measurement range |
Select the range of the input signal to be measured. |