CSS Toggle
Based on the HACCP food hygiene management method, the ISO22000 of a food safety management system that enables the provision of safe food to consumers, as well as compliance with international certifications such as GAP, which regulates production control such as the use of pesticides, are conditions for imports and transactions overseas.
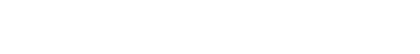
HACCP is a hygiene management method in which food and other business operators identify hazards such as contamination with food poisoning bacteria and foreign matter and manage process, which are particularly important for eliminating or reducing these hazards, from the arrival of raw materials to the process shipment of products, and to ensure product safety.
This approach was published by the Food Standards (Codex) Committee, a joint agency of the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) and the World Health Organization (WHO), and is internationally recognized and recommended for adoption by countries.
HACCP provides a variety of guidelines to follow, one of which is proper temperature control of food. For example, proper temperature control is an important factor in a variety of equipment, such as a refrigerator in the kitchen of a restaurant, a refrigerated case in a supermarket, or the core temperature of food during the cooking process during the manufacturing process in a food factory.
Hygiene management incorporating HACCP concepts
Hygiene management that incorporates the HACCP concept is based on the three principles of food poisoning prevention (don't let harmful microorganisms get in, don't let them grow, and eliminate them), and involves clarifying, implementing, and recording the hygiene management that you are currently working on and the points to be aware of according to the menu in advance as a hygiene management plan. It is not a completely different response from before, but rather makes hygiene management "visible" through plans and records.
In addition, when HACCP is implemented, temperatures must be recorded and stored, and methods must be established to monitor whether they are being properly controlled.
The revised Food Sanitation Act, passed in June 2018, has made it mandatory for all food businesses to introduce hygiene management standards based on HACCP from June 2020. There will be a one-year grace period after the 2020 law comes into force, and the law will be fully implemented from June 2021.
process Examples
The danger temperature range for food is between 10℃ and 60℃. This temperature is a very comfortable environment for bacteria. In other words, if food remains at this temperature, it will cause bacteria to multiply rapidly.
Temperature control pointer in HACCP
1st GROUP [Cuisine that does not require heating]Because there is no cooking process, harmful microorganisms that may be present in the ingredients cannot be killed.
Therefore, it is important to use ingredients that are not contaminated by harmful microorganisms, or to store them in the refrigerator (low temperature) to prevent the proliferation of harmful microorganisms that may have been contaminated. It is important to store them in the refrigerator (below 10°C) or freezer (below -15°C).
2nd GROUP [Food that is heated and served]Be sure to cook meat such as chicken thoroughly, as it may be contaminated with harmful microorganisms.
Many harmful microorganisms present in meat and other foods are killed when heated to 75°C for at least one minute. For this reason, it is important to cook meat thoroughly.
Also, after cooking, be careful not to contaminate food with your hands or cooking utensils (including plates) when plating the food.
It is important that the core temperature reaches the specified value (75°C for 1 minute).
3rd GROUP [Food that is cooked, cooled and then reheated or cooked and cooled]If cooked food is left at room temperature for a long time, harmful microorganisms that remain in the food or that attach to the food after heating will multiply, which can cause food poisoning.
When storing after heating, it is important to store it at 60°C or above, or to cool it quickly to avoid it remaining in the danger temperature zone (10-60°C) for a long time.
We propose a hygiene management system that incorporates HACCP principles based on temperature measurement and temperature calibration technology.
Source: Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare website
Heat sterilization with F value control
For canned foods and retort foods, a method of managing the F value is used during heat sterilization. The F value indicates the effect (strength) of heat sterilization, and its calculation includes temperature and heating time. The "Retort Temperature Sensor C030" is a sensor suitable for measuring the ambient temperature and actual temperature of food during sterilization to calculate the F value.
We also offer accessories can be easily attached to packs and cans.
We also offer the "high-temperature drip-splash-proof resistance thermometer R906-3," which can be inserted into high-temperature water vapor atmospheres, including the lead wires.
In addition, for heat sterilization, autoclaves (high pressure steam sterilizers) and other devices are used to maintain temperatures for a certain period of time, such as our graphic programmable controller DP-G series. The F value can be directly managed using computation function of the graphic recorder KR2S. computation formula is registration in the KR2S, so the F value can be easily display.
Related product
 |
Retort Temperature Sensor
C030
 Click here for detailed specifications Click here for detailed specifications
|
It is suitable for measuring the ambient temperature and actual temperature of food during sterilization in order to computation the F value, which indicates the heat sterilization effect of canned foods, retort foods, etc. |
 |
High temperature splash-proof-proof resistance thermometer
R906-3
 Click here for detailed specifications Click here for detailed specifications
|
This is a splash-proof-proof sensor that uses fluororesin-coated conductors for the lead wires, and can be inserted into high-temperature water vapor atmospheres, including the lead wires. It is suitable for sterilization pots for heat sterilization and for measuring F values. |
 |
FKA (Canned Food Adapter)
FPA (Fuck adapter)
*Please contact our sales office. |
|
 |
Graphic recorder
KR2S00 Series
 Click here for detailed specifications Click here for detailed specifications
|
This is a 144 x 144 mm paperless recorder that pursues cost performance. |
 |
Graphic program controller
DP-G Series
 Click here for detailed specifications Click here for detailed specifications
|
The DP-G series uses a 5.6-inch color LCD display in the display with an accuracy of 0.1% and a sampling period of 0.1 seconds, which makes the operation display and setting operation more visualized, and the monitor screen is also enhanced. |
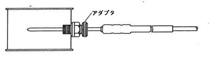
We not only provide sensors, but also propose temperature monitoring systems. Automating the process using the MD8000 series wireless devices and the CISAS recording and monitoring system reduces the load and prevents human error.
With remote monitoring, email notification in the event of an abnormality (buzzer and abnormal light also supported), and easy-to-understand visualization of the system on a graphic screen, you can build a safe and secure temperature monitoring system.
Also, in work sites that are humid due to steam, etc., why not also monitor the heat index WBGT and manage operator safety at the same time?
Related product
 |
Wireless logger with monitoring function
(Receiver supports Ethernet connection)
MD8000 Series
Wireless Watcher
 Click here for detailed specifications Click here for detailed specifications
|
- Data from 360 transmitters can be centrally managed using a single computer.
- The radio wave reach is approximately 100m indoors and 400m outdoors.
- application software is also available *.
*Special PC software sold separately. |
 |
Recording and monitoring package system
CISAS/V4
 Click here for detailed specifications Click here for detailed specifications
|
This package system uses our recorders, loggers, and controllers, as well as commercially available PLCs (programmable controllers), as system components and can collect and monitor data from up to 5,000 tags of various devices and equipment on a PC. |
We can propose temperature sensors, regulators, recorders and monitoring systems according to customer requests.
First, please contact your nearest sales office or contact us via our inquiry form.
Related product
A full lineup of temperature sensors, accessories and solutions
 |
Retort Temperature Sensor
C030
 Click here for detailed specifications Click here for detailed specifications
|
It is suitable for measuring the ambient temperature and actual temperature of food during sterilization in order to computation the F value, which indicates the heat sterilization effect of canned foods, retort foods, etc. |
 |
FKA (Canned Food Adapter)
FPA (Fuck adapter)
*Please contact our sales office. |
|
A lineup of controllers suitable for equipment, from large to small
 |
Digital indicating controller
DB600 Series
 Click here for detailed specifications Click here for detailed specifications
|
The DB600 series is a digital indicating controller with display accuracy of ±0.1% and control cycle of 0.1 seconds. display uses a bright, large LCD with a wide field of view angle, making display easy to see and understand. The control method can be selected from PID control or our unique Z control algorithm according to the target. Three sizes are available to suit the site of use, and the depth is shorter than conventional products. |
 |
Graphic program controller
DP-G Series
 Click here for detailed specifications Click here for detailed specifications
|
The DP-G series uses a 5.6-inch color LCD display in the display with an accuracy of 0.1% and a sampling period of 0.1 seconds, which makes the operation display and setting operation more visualized, and the monitor screen is also enhanced. |
recorder and equipment that can measure HACCP-related parameter such as F values, as well as wireless devices and measurement systems that consolidate measurements from the entire factory
 |
Graphic recorder
KR2S00 Series
 Click here for detailed specifications Click here for detailed specifications
|
This is a 144 x 144 mm paperless recorder that pursues cost performance. |
 |
Wireless logger with monitoring function
(Receiver supports Ethernet connection)
MD8000 Series
Wireless Watcher
 Click here for detailed specifications Click here for detailed specifications
|
- Data from 360 transmitters can be centrally managed using a single computer.
- The radio wave reach is approximately 100m indoors and 400m outdoors.
- application software is also available *.
*Special PC software sold separately. |
 |
Recording and monitoring package system
CISAS/V4
 Click here for detailed specifications Click here for detailed specifications
|
CISAS/V4 is a package system that uses our recorders, loggers, and controllers, as well as commercially available PLCs (programmable controllers), as system components to collect and monitor data from up to 5,000 tags of various devices and equipment on a PC. |
- General Hygiene Management Programs: (Prerequisite Programs: PRP)
A hygiene management program for food handling facilities that is a prerequisite for the HACCP system to function effectively. It is also called a prerequisite program. The "General Principles of Food Hygiene" set forth by the Codex Alimentarius Commission is the basis, and examples of this include "Business Establishment Standards" and "Management and Operation Standards" established by local government ordinances. - Sanitation Standard Operation procedure: SSOP
A documented sanitation management procedure that clearly describes "when, where, who, what, and how to do it." A sanitation management procedure requires daily inspection as part of general sanitation management. - Hazard:
A substance in or condition of food that can cause an adverse health effect (harm). Also called a hazard. It can be biological, chemical, or physical, such as harmful microorganisms, chemicals, or hard foreign bodies. - Hazard Analysis:
By collecting and evaluating information on hazards and the conditions under which they occur, potential hazards present in foods throughout the process, from raw material production through manufacturing, processing, and distribution to consumption, are clarified, including the likelihood of the hazards occurring and their severity if they do occur, and further, the control measures for each hazard are clarified. - Control measure:
A procedure or action used to prevent or eliminate a hazard, or to reduce it to an acceptable level. Also called a control measure. - Critical Control Point (CCP):
A step that requires particularly strict control and is essential for preventing or eliminating hazards in food, or reducing them to an acceptable level in order to prevent the occurrence of hazards. Also called a critical control point. - Management criteria (Critical Limit: CL):
The limit of parameter that distinguishes between acceptable and unacceptable levels of hazard control. Also called critical limit. - Monitoring:
Observations, measurements, and tests conducted to determine whether a CCP is under control. - Corrective Action:
Measures to be taken when parameter deviates from the control standard as a result of monitoring at a CCP. Also called corrective measures. - Verification:
The methods, procedures and tests used to determine whether the HACCP plan is being followed or whether the HACCP plan needs modification. This is in addition to monitoring. - Validation:
To gather evidence that the HACCP plan is designed correctly and that the elements of the HACCP plan are effective. - HACCP plan:
A plan prepared in accordance with the principles of HACCP system application to control significant hazards related to food safety in the target food process (production, manufacturing, distribution, etc.). - PDCA Cycle
It involves making a plan for hygienically manufacturing and processing food (Plan), execution the manufacturing and processing in accordance with the plan (Do), verifying that the operations are being carried out in accordance with the plan (Check), and investigating and taking action (Act) in any areas where operations are not in accordance with the plan. This is a four-step process (PDCA), and the final "action" (Act) leads to the next cycle, with the content improved with each cycle to ensure continuous improvement of operations.
Source: Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare website
The health functional food system is a system that allows foods that meet the safety and effectiveness standards set by the government to be display as health functional foods. Previously, there were only two types of foods: Foods for Specified Health Uses (commonly known as Tokuho), which were approved under national review by showing scientific evidence of efficacy and safety, and Foods with Nutrient Function Claims, which met the standards for specific nutritional constituent set by the government, but in 2015, display food was newly added.
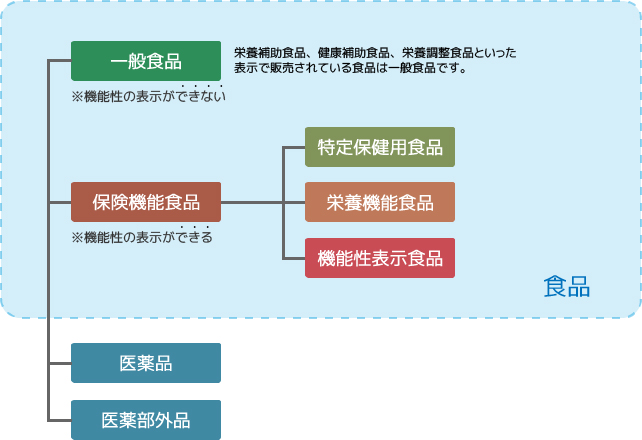
On July 1, 2019, the Consumer Affairs Agency revised the "Guidelines for display of Functional Foods" and the "Questions and Answers on display Foods." Functional foods display functionality at their own responsibility if they notify the Commissioner of the Consumer Affairs Agency of necessary information, such as scientific evidence regarding the safety and functionality of the food, based on rules set by the government. The information notified to the Consumer Affairs Agency is published on the Consumer Affairs Agency's website, allowing all consumers to display how the functionality and safety of food is ensured.
Hygiene and quality control system
In order to sell display foods, it is necessary to establish and explain a system that ensures safety from the viewpoint of hygiene management and quality control during production and manufacturing. For this reason, display food businesses that sell functional foods are strongly encouraged to obtain certifications such as GMP, HACCP, ISO22000, and FSSC22000, and especially for processed foods in the form of supplements, it is highly recommended that they manage their manufacturing process based on GMP. In addition, for fresh foods, homogeneity and the establishment of a management system for it are required.
Temperature control for display foods
Temperature control is important for hygiene management and quality maintenance of functional foods. HACCP, ISO22000, and FSSC22000 require the establishment of mandatory process (CCP: Critical Control Points) for managing important hazards to quality, regular temperature display, and the establishment of a system for prompt response when an abnormality occurs. Temperature records must also be kept, and procedure for doing so must also be established. Furthermore, GMP requires that temperature monitoring and record management be managed in accordance with the requirements of FDA21CFR Pert11 and ER/ES pointer. As mentioned above, it takes a lot of effort to steadily execution temperature control. Doing it manually requires even more effort and there are concerns about reliability.