Temperature and Humidity Standards
1. SI unit
The international unit system is built on the basis of seven quantities, length, mass, time, current, unit, which are clearly defined for thermodynamic temperature, amount of matter and luminous intensity, meter (m), kilogram (kg), second (s), ampere (A), kelvin (K), mole (mol), candela (cd). These unit are called base unit (base units), and unit other than base unit are defined by the combination of multiple base unit, which are called assembly unit (deriverd units).
The base unit for temperature is K (Kelvin), which is defined by "Kelvin is defined by determining the Boltzmann constant value to be exactly 1.380 649
×10-23J/K." It is.
The relationship between the thermodynamic temperature T and the Celsius temperature t is the same magnitude when the temperature difference is expressed by the following equation, only the reference point is different.
t/℃=T/K-273.15
2. ITS-90
The International Temperature scale defines the thermodynamic temperatures of the vapor pressure point, triple point, melting point, and freezing point of various substances based on the triple point of water, and scale currently in use is the ITS-90 (International Temperature Scale of 1990), which was established in 1990.
At the same time, the International Temperature scale specifies an interpolation instrument and an interpolation formula for interpolating temperature scale between fixed points.
Note: The International Temperature scale is reviewed approximately every 20 years, and the previous standard was the IPTS-68 (International Practical Temperature Scale of 1968), which was established in 1968.
3. Triple point of water
This is usually achieved in a glass cell filled with distilled water, where all three states of water (solid, liquid, and gas) exist simultaneously.
 | 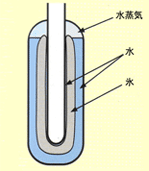 | 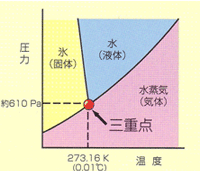 |
| The temperature at the point where the three phases meet is 273.16K. | Phase diagram of water
The state where three phases of water - solid (ice), liquid (water), and gas (water vapor) - coexist is called the triple point of water. |
4. Traceability System
The national standard for temperature is the device that realizes the temperature fixed point specified in ITS-90, and is owned by the National Institute of development Industrial Science and Technology. The traceability system diagram is shown below.
5. Calibration method
- Fixed-point calibration method
This is done using a "fixed-point achieving device" that combines a fixed-point cell filled with high-purity metal, a temperature regulator, and a heating or cooling device to achieve the triple point, freezing point, or melting point specified in ITS-90.
Calibration is mainly carried out by standards research institutes and thermometer calibration businesses for the purpose of scale standard thermometers.
Features
- Small calibration uncertainty
- Standard thermometer is usually not required
- Only certain temperatures can be calibrated
- Comparison Calibration Method
For contact thermometers, an oil bath or electric furnace is used, while for radiation thermometer, a temperature generating device such as a variable temperature blackbody furnace is used, and the temperature is measured by comparing it with a pre-calibrated standard thermometer.
It is primarily used by thermometer calibration businesses and thermometer users to calibrate field level thermometers.
Features
- Large calibration uncertainty
- A standard thermometer is required
- Calibration possible at arbitrary temperature
1. What is humidity?
There are various ways to express humidity, and "JIS Z 8806 Humidity - Measurement methods" lists the following a) to i).
a) Mixing ratio r (kg/kg): Ratio of the mass of water vapor in wet air to the mass of dry air
b) Molar fraction xv (mol/mol) is the ratio of the amount of water vapor in moist air to the total amount of
c) Specific humidity q (kg/kg): The ratio of the mass of water vapor in moist air to the total mass (mass fraction)
d) water vapor pressure e (Pa) Partial pressure of water vapor in moist air
e) Absolute humidity dv (kg/cm3) is the mass of water vapor in unit volume of moist air
f) Relative humidity Uw (%) is 100 times the ratio of the mole fraction of water in moist air xv to the mole fraction of water in moist air saturated at that temperature and pressure xvs
g) Comparative humidity Ψ (%) 100 times the ratio of the mixture ratio r of moist air to the mixture ratio rs of moist air saturated at that temperature and pressure
h) Dew point td (℃) The temperature at which the saturated vapor pressure of water is equal to the water water vapor pressure in moist air.
i) Frost point tf (℃) is the temperature at which the saturated vapor pressure of ice is equal to water vapor pressure in moist air.
Relative humidity is commonly used to express this, and in practice the following formula using water vapor pressure is used instead of the above f).

Saturation water vapor pressure = partial pressure of vapor when air contains the maximum amount of moisture (vapor) at a certain temperature
2. Traceability System
3. Calibration method
Calibration of a hygrometer is usually performed by obtaining the relative humidity of the humidity generating chamber using a dew point meter and a thermometer, and comparing it with the hygrometer to be calibrated, as shown in the figure below.
The relationship between temperature and water vapor pressure is given by the SONNTAG equation.
From the above formula, the saturated vapor pressure
ewT at the temperature T indicated by the thermometer and the dew point temperature
ewT0 indicated by the dew point meter can be calculated, so the relative humidity
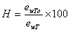
is obtained.