"Measure temperature" Body temperature, air temperature, hot water temperature, indoor temperature, etc.
Everyday, we measure temperature in various places and see measured temperature values. But how is temperature measured?
 First of all, what exactly is temperature?
First of all, what exactly is temperature?
Temperature is a quantity proportional to the average kinetic energy of the molecules or atoms in an object. In other words, temperature is one measure of the strength of kinetic energy. The stronger the energy, the higher the temperature, and the weaker the energy, the lower the temperature.
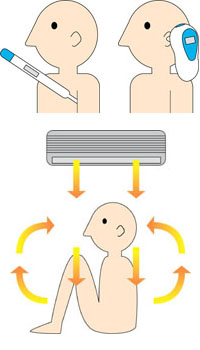 So how is the temperature measured?
So how is the temperature measured?
Temperature is measured by the transfer of heat from the object being measured to the temperature sensor. There are three phenomena involved in the transfer of heat: 1) thermal conduction, 2 thermal radiation and 3) convection.
First, ①thermal conduction is the transfer of vibration energy from a high-temperature object to a low-temperature object. A "thermometer" that measures air temperature and a "thermometer" that measures body temperature can read the temperature by transmitting the surrounding air temperature and body temperature to the thermometer, which becomes the same temperature as the thermometer. Contact-type thermometers such as thermocouples, which are called temperature sensors, measure temperature using this thermal conduction.
②Heat thermal radiation is the movement of electromagnetic waves from a hot object to a cold object. thermal radiation to radiation thermometer, and like an "ear thermometer," it captures the heat energy coming from inside the ear to measure temperature without contact.
The remaining ③ convection is the movement of the object itself in the spatial temperature distribution. Convection is not used for temperature measurement because it is difficult to establish a stationary relationship between the measurement object and the temperature sensor, and the aforementioned thermal conduction and thermal radiation are often used instead.
thermal radiation (infrared)
thermal radiation spans the ultraviolet, visible light, and infrared regions (Figure 1). The laws governing thermal radiation were formulated by Planck (Planck's law of radiation).
The diagram below (Figure 2) shows that, first, as the temperature of an object increases, thermal radiation energy emitted from the object becomes stronger, and second, as the temperature of an object increases, the wavelength distribution of thermal radiation energy shifts toward shorter wavelengths.
Why are radiation thermometer useful?
- high-speed temperature measurement possible
Temperature measurement using thermal conduction is a method in which heat conduction occurs when the object being measured comes into contact with the object acting as the temperature sensor, and when the temperature of the object acting as the sensor becomes the same as the temperature of the object being measured, the temperature is calculated by capturing the changes in the properties exhibited by the object acting as the sensor, but due to thermal capacity, it takes a certain amount of time for the two to become the same temperature.In contrast, radiation thermometer transmit thermal radiation at the speed of light, making it possible to measure temperature at high-speed.
- Non-contact temperature measurement is possible
The advantages of non-contact temperature measurement include "remote measurement" and "measurement without causing thermal agitation."
"Remote sensing" includes "long-distance measurements," such as measuring the temperature of clouds from the ground, "isolated measurements," such as measuring the temperature inside a furnace through a window, "measurement of moving objects," and "measurement of high-temperature objects," in which the sensor part of a thermometer that uses thermal conduction would melt.
On the other hand, "measurement without thermal agitation" means that with a thermometer that uses thermal conduction, the temperature of the object being measured changes when the sensor comes into contact with the object being measured (measurement that causes thermal agitation), and accurate measurement may not be possible, whereas with radiation thermometer, the temperature of the object being measured does not change. Therefore, it is effective for measuring objects with small heat capacity such as film and for measuring the surface temperature of metals.
emissivity
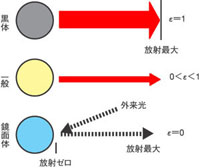
emissivity is the ratio of thermal radiation emitted from an object to a perfect radiator. An ideal object that radiates the most has emissivity of 1 and is called a "perfect radiator" or "blackbody." An object that does not radiate itself and completely reflects thermal radiation from its surroundings has emissivity of 0 and is called a specular body. emissivity of a general object is between 0 and 1. emissivity of metals tends to be higher the shorter the measurement wavelength and lower the longer the wavelength. The value varies depending on the surface properties even for the same material, such as the same material tending to have a higher emissivity if the surface is rough. Also, Planck's law of radiation, which we discussed in "thermal radiation," assumes that the object is blackbody.
Classification of radiation thermometer
Focusing on the fact that radiant energy becomes stronger as temperature increases, the type that determines temperature by measuring the strength of energy is called an "energy intensity type." Focusing on the fact that wavelength distribution shifts to the short wavelength side as temperature increases, the type that determines temperature by measuring the change in wavelength distribution is called a "wavelength distribution type."
- Energy Intensity Type
Among energy intensity thermometers, those that calculate the temperature from the integral value over the entire wavelength range are called "total radiation thermometer" (types where energy is proportional to the fourth power of thermodynamic temperature). In reality, it is difficult to measure the entire wavelength range due to constraints such as the wavelength selectivity of detecting element and optical materials, so the measurement wavelengths that are advantageous for measurement are limited to a certain extent by using atmospheric windows, and these are called "broadband radiation thermometer." Among energy intensity thermometers, those that calculate the temperature from the radiant energy intensity at a single wavelength are called "single-color thermometer," and those that calculate the temperature from the radiant energy intensity in a relatively narrow wavelength range are called "narrowband radiation thermometer." - Wavelength distribution
Among the "wavelength distribution" types, the type that measures the radiant energy at two wavelengths to capture the wavelength distribution and measures the temperature from the ratio is called a "two-color thermometer."
radiation thermometer structure
radiation thermometer consists of three elements: a "light collecting system" that captures light, a "photoelectric conversion system" that converts the captured light into an electrical signal, and an "electrical system" that configuration the converted electrical signal as a signal corresponding to temperature.
fixed focus type/ focusable type
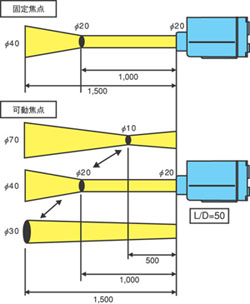
A type that adjusts the lens focus to match the distance between radiation thermometer and the object to be measured is called focusable type, while a type that does not require focusing is called fixed focus type.
Size and distance of the object to be measured
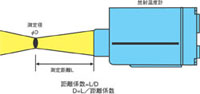
Select the model by checking the distance between radiation thermometer and the object to be measured, and the size of the object to be measured. A guideline for the relationship with the size of the object to be measured is 1.5 times or more the measurement diameter. For focusable radiation thermometer, the measurement distance/measurement diameter is called distance factor, and if you want to measure a 10mm size at a distance of 1000mm, select radiation thermometer with distance factor of 100. distance factor of 50, 100, 200, 300, etc. are available. The minimum target size is about 2mm, and if you want to make it even smaller, you can use a close-up lens. For fixed focus radiation thermometer select models from the relationship diagram between target size and distance.
Detecting element
The "photoelectric conversion system" converts the light captured by light collecting system (lens, mirror, fiber optics) into an electrical signal. This device is called a "detecting element." There are two types of detecting element: photoelectric, which uses the fact that the electrical properties of the element change directly in response to the optical signal, and thermoelectric type which first receives the optical signal as heat and then uses that thermal change.
| Classification | principle | Wavelength characteristic | responsiveness | Representative examples detecting element |
|---|
| thermoelectric type | Light → Heat → Electricity | Flat type | slow | pyroelectric element (PE), thermopile |
| Photoelectric Type | Light → Electricity | Yamagata | fast | PbSe, PbS, Ge, MCT, InGaAs, Si |
Lens integrated type and fiber optics type
radiation thermometer The fiber optics type, in which the condenser lens (light collecting system) that captures thermal radiation is usually integrated with the main body (photoelectric conversion system + electrical system), but the condenser lens is separated from the main body and connected to it by fiber optics, is also available. fiber optics The features type has a small tip, a flexible light path, and can be used in explosion proof atmospheres where it is less susceptible to electromagnetic induction influences.
lack of view
If an object obstructs sight path of radiation thermometer, thermal radiation energy decreases, resulting in an error in the reading. This is called lack of view.