1. Light (electromagnetic waves)
Light and infrared rays are types of electromagnetic waves with various wavelengths. These electromagnetic waves are caused by the flow (vibration) of electric charges (current) generating a magnetic field around it, and the fluctuation of this magnetic field generates a new electric field, and these fields link together one after another while traveling in directions perpendicular to each other. This phenomenon is called electromagnetic waves.
Furthermore, in a vacuum, these electromagnetic waves always travel in a straight line at a constant speed of about 300,000 km per second.
2. Wavelength, vibration, and Wave Number (Kaiser)
Electromagnetic waves (light) are caused by vibration of electric charges, so vibration indicates how many times that vibration vibration per second.
Wavelength is unit that represents the length of one period of vibration, and is expressed as "speed of light / vibration." Wave number (Kaiser) is the number of waves (vibration) per centimeter, and is expressed as wave number = 1 / wavelength (cm).
When describing characteristic of light, this wavenumber (Kaiser, cm^-1) seems to be more commonly used than wavelength.
3. What is infrared?
Infrared light is a type of light (electromagnetic waves) that generally has a wavelength range of 0.75 to 200 µm, which is longer than visible light.
Furthermore, the infrared light that is close to visible light, around 0.75 to 3 µm, is called near-infrared light (refer below).
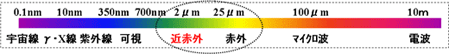
4. features of various electromagnetic waves (light)
The properties of electromagnetic waves (light) vary depending on their wavelength. Generally, the shorter the wavelength, the greater the energy.
Long-wavelength radio waves (used in familiar devices such as televisions, radios, and cell phones) vibrate the electrons in metals such as antennas, generating an electric charge (current).
Infrared rays, which have shorter wavelengths, generate heat by vibration various molecules, while microwaves cause moisture (H2O) to rotation (as used in microwave ovens).
Visible light stimulates (vibration) the red, green, and blue sensitive cells in the human retina, enabling us to perceive color.
In addition, ultraviolet rays with short wavelengths excite electrons and cause chemical reactions (such as sunburn and inflammation), and X-rays have strong penetrating properties (used in X-rays, etc.) and can cause ionization of gases, photoelectric effects, chemical reactions, and deterioration of biological tissue.
Furthermore, gamma rays, which have a shorter wavelength, have stronger penetrating characteristic than X-rays and can cause atomic ionization, the emission of secondary electrons, and so on.