| low-order communication | Imports input data from devices connected to the recorder. |
|---|
| remote contact | A function that allows remote control operation such as starting and stopping recording using external non-voltage contact signals. |
|---|
| External memory | Used to store measurement data.
CF cards, USB memory, etc. are called external memory (⇔ internal memory). |
|---|
| Automatic scale switching by location |
This is a dot printing type recorder with two measurement ranges. The measurement locations are divided into two groups, and the measurement range is switched periodically for each group.
For example, on a 6-point recorder, points 1 to 3 are used for 0 to 600°C, and points 4 to 6 are used for 0 to 1200°C.
 |
| Range by location | The hybrid recorder KH and KL series are dot printing type-printing specifications, and the input type and measurement range can be designate for each channel. |
|---|
| Paper feed speed (chart speed) | chart paper advance speed |
|---|
| Reference measurement range (= reference range) | The input range that is actually used when the input type is set.
The range setting automatically switches depending on the range number. |
|---|
Reference point compensation (RJ)
reference junction compensation accuracy | This refers to the function and accuracy that enables measurements without an external reference contact compensator when connecting a thermocouple to the input terminal. Accuracy differs depending on the thermocouple. |
|---|
| reference operating condition | Conditions for satisfying accuracy ratings stated in the catalog, etc. |
|---|
| recording intervals | Set the interval at which data is recorded. |
|---|
| Graphic recorder | Paperless recorder. Measurement data is display on the LCD screen and stored in memory. |
|---|
| Group Function | A function that handles multiple channel together. You can switch display for each group and configure group settings. |
|---|
| Alarm function | When the value of the measurement data exceeds the alarm setting value, an alarm judgment (a contact) is made. |
|---|
| Alarm deadband | A function that prevents alarms from being issued and reset frequently when the measured value is fluctuating repeatedly. |
|---|
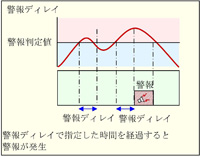
| Alarm delay | Even if the measured value exceeds the alarm setting value, the alarm is not generated immediately, but is generated after the alarm delay time has elapsed.
 |
|---|
| high-speed dot printing type | option makes dot printing type interval of the dot printing type recorder approximately 2.5 seconds. The specifications dot printing type interval is approximately 5 seconds. |
|---|